How Logistics Keeps Global Trade Moving Behind the Scenes
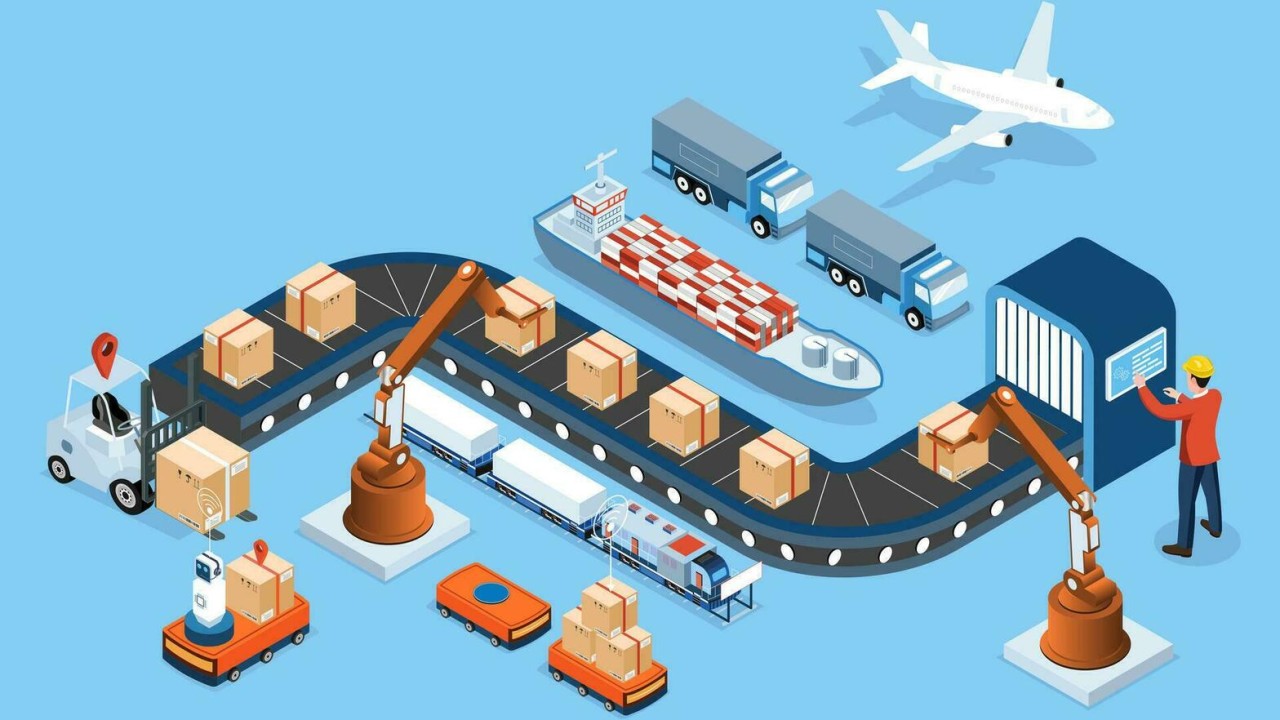
Logistics is the silent engine powering global trade. It works behind the scenes, coordinating people, processes, infrastructure, and technology to ensure goods move efficiently from producers to consumers. Without logistics, international trade would grind to a halt. In this article, we explore how logistics keeps global trade moving, the key components involved, the challenges faced, and why efficient logistics is more important today than ever before.
Understanding Logistics in Global Trade
At its core, logistics is the planning, execution, and management of the movement and storage of goods, services, and information from origin to destination. In global trade, logistics goes far beyond transportation. It includes:
- Procurement and sourcing
- Warehousing and inventory management
- Transportation (air, sea, road, and rail)
- Customs clearance and documentation
- Freight forwarding
- Distribution and last-mile delivery
Each of these elements must work in harmony to ensure goods arrive at the right place, at the right time, in the right condition, and at the right cost.
The Invisible Journey of Goods
When a product is manufactured, its journey has only just begun. A single shipment may pass through multiple stages:
- Factory or supplier pickup
- Local transportation to a port or warehouse
- Export documentation and customs processing
- International transportation
- Import customs clearance
- Warehousing at destination
- Final delivery to retailers or consumers
Behind each stage is a network of logistics professionals—planners, freight forwarders, customs brokers, warehouse operators, and drivers—working together to prevent delays, reduce costs, and manage risks.
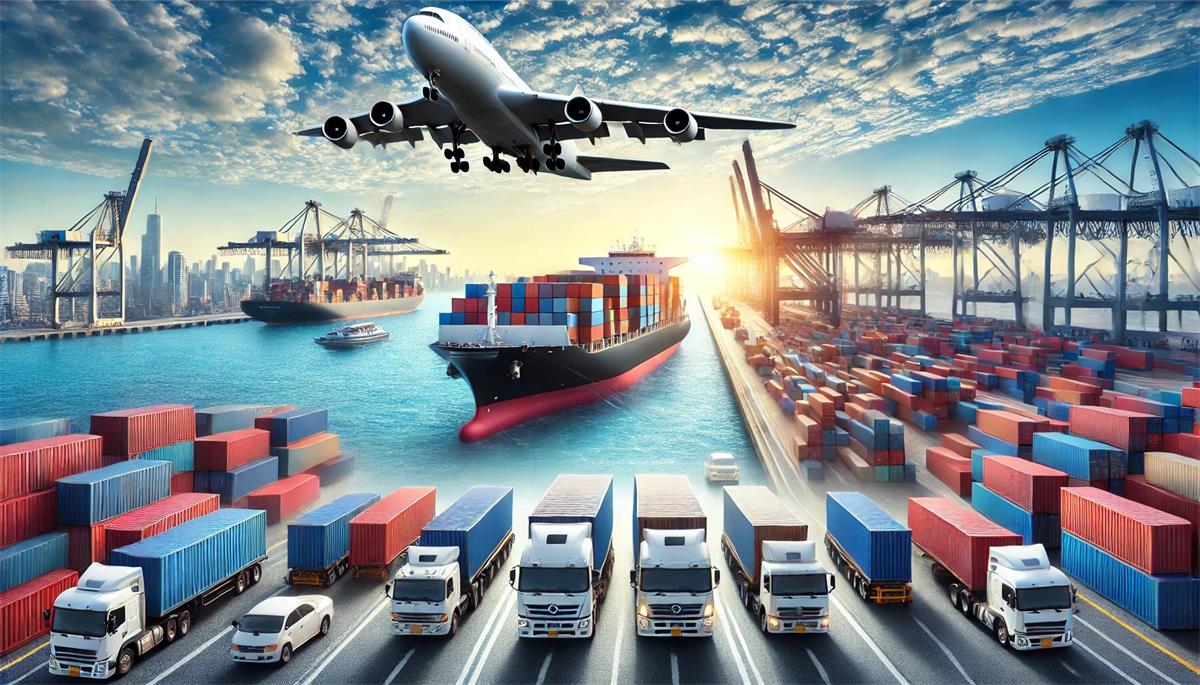
Transportation: The Backbone of Logistics
Transportation is the most visible part of logistics, yet much of its complexity happens behind the scenes. Global trade relies on four major modes of transport:
1. Sea Freight
Over 80% of global trade by volume is transported by sea. Container ships move massive quantities of goods across oceans at relatively low cost. Logistics providers coordinate vessel schedules, container availability, port operations, and cargo consolidation to ensure efficiency.
2. Air Freight
Air freight is used for high-value, time-sensitive, or perishable goods. Although more expensive, it plays a critical role in industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and fashion.
3. Road Transport
Road transport connects ports, warehouses, factories, and final destinations. It is essential for both domestic logistics and cross-border trade within regions.
4. Rail Transport
Rail offers a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option for long-distance inland transportation, especially in regions with strong rail infrastructure.
Warehousing: More Than Storage
Warehouses are not just storage spaces; they are strategic hubs in global trade. Modern warehousing involves:
- Inventory control and stock optimization
- Order picking and packaging
- Cross-docking to reduce storage time
- Value-added services such as labeling or assembly
Customs and Documentation: Navigating Global Regulations
One of the most critical yet least visible aspects of logistics is customs compliance. Every international shipment must comply with the laws and regulations of both exporting and importing countries.
- Commercial invoices
- Packing lists
- Bills of lading or airway bills
- Certificates of origin
- Import/export permits
- Duties and taxes calculation
Freight Forwarders: The Orchestrators of Global Trade
Freight forwarders play a central role in logistics. They coordinate all logistics elements and ensure seamless movement of goods across borders.
Technology: The Digital Backbone of Modern Logistics
Technology has transformed logistics into a industry, enabling real-time tracking, predictive analytics, and operational efficiency.
Risk Management and Problem Solving
Logistics teams manage risks such as port congestion, weather disruptions, political instability, and regulatory changes to keep trade flowing smoothly.
Logistics and Global Economic Growth
Efficient logistics drives economic growth by reducing trade costs, improving market access, and increasing competitiveness.
Sustainability in Logistics
The logistics industry is adopting sustainable practices such as optimized routing, eco-friendly packaging, and cleaner transport modes.
The Human Element Behind Logistics
Despite automation, logistics depends heavily on skilled professionals who ensure smooth operations across the supply chain.
Why Logistics Matters More Than Ever
With e-commerce growth and global supply chain complexity, logistics has become essential for speed, transparency, and resilience.
Conclusion: The Silent Force Powering the World
Logistics may operate behind the scenes, but it is the force that keeps global trade alive—connecting economies, supporting businesses, and delivering goods worldwide.